Quick Start
Before proceeding, please ensure you have installed GreptimeDB.
This guide will walk you through creating a metric table and a log table, highlighting the core features of GreptimeDB.
Connect to GreptimeDB
GreptimeDB supports multiple protocols for interacting with the database. In this quick start document, we use SQL for simplicity.
If your GreptimeDB instance is running on 127.0.0.1 with the MySQL client default port 4002 or the PostgreSQL client default port 4003,
you can connect to GreptimeDB using the following commands:
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 4002
Or
psql -h 127.0.0.1 -p 4003 -d public
Create tables
Suppose you have a table named grpc_latencies that stores the gRPC latencies of your application.
The table schema is as follows:
CREATE TABLE grpc_latencies (
ts TIMESTAMP TIME INDEX,
host STRING,
method_name STRING,
latency DOUBLE,
PRIMARY KEY (host, method_name)
)
engine=mito with('append_mode'='true');
ts: The timestamp when the metric was collected. It is the time index column.host: The hostname of the application server. It is a tag column.method_name: The name of the RPC request method. It is a tag column.latency: The latency of the RPC request.
Additionally, there is a table app_logs for storing application logs:
CREATE TABLE app_logs (
ts TIMESTAMP TIME INDEX,
host STRING,
api_path STRING FULLTEXT,
log_level STRING,
log STRING FULLTEXT,
PRIMARY KEY (host, log_level)
)
engine=mito with('append_mode'='true');
ts: The timestamp of the log entry. It is the time index column.host: The hostname of the application server. It is a tag column.api_path: The API path, indexed withFULLTEXTfor accelerated search..log_level: The log level of the log entry. It is a tag column.log: The log message, indexed withFULLTEXTfor accelerated search.
Write data
Let's insert some mocked data to simulate collected metrics and error logs.
Two application servers, host1 and host2,
have been recording gRPC latencies. Starting from 2024-07-11 20:00:10,
host1 experienced a significant increase in latency.
The following image shows the unstable latencies of host1.
The following SQL statements insert the mocked data.
Before 2024-07-11 20:00:10, the hosts were functioning normally:
INSERT INTO grpc_latencies (ts, host, method_name, latency) VALUES
('2024-07-11 20:00:06', 'host1', 'GetUser', 103.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:06', 'host2', 'GetUser', 113.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:07', 'host1', 'GetUser', 103.5),
('2024-07-11 20:00:07', 'host2', 'GetUser', 107.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:08', 'host1', 'GetUser', 104.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:08', 'host2', 'GetUser', 96.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:09', 'host1', 'GetUser', 104.5),
('2024-07-11 20:00:09', 'host2', 'GetUser', 114.0);
After 2024-07-11 20:00:10, host1's latencies becomes unstable:
INSERT INTO grpc_latencies (ts, host, method_name, latency) VALUES
('2024-07-11 20:00:10', 'host1', 'GetUser', 150.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:10', 'host2', 'GetUser', 110.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:11', 'host1', 'GetUser', 200.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:11', 'host2', 'GetUser', 102.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:12', 'host1', 'GetUser', 1000.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:12', 'host2', 'GetUser', 108.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:13', 'host1', 'GetUser', 80.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:13', 'host2', 'GetUser', 111.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:14', 'host1', 'GetUser', 4200.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:14', 'host2', 'GetUser', 95.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:15', 'host1', 'GetUser', 90.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:15', 'host2', 'GetUser', 115.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:16', 'host1', 'GetUser', 3000.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:16', 'host2', 'GetUser', 95.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:17', 'host1', 'GetUser', 320.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:17', 'host2', 'GetUser', 115.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:18', 'host1', 'GetUser', 3500.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:18', 'host2', 'GetUser', 95.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:19', 'host1', 'GetUser', 100.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:19', 'host2', 'GetUser', 115.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:20', 'host1', 'GetUser', 2500.0),
('2024-07-11 20:00:20', 'host2', 'GetUser', 95.0);
Some error logs were collected when the host1 latencies of RPC requests encounter latency issues.
INSERT INTO app_logs (ts, host, api_path, log_level, log) VALUES
('2024-07-11 20:00:10', 'host1', '/api/v1/resource', 'ERROR', 'Connection timeout'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:10', 'host1', '/api/v1/billings', 'ERROR', 'Connection timeout'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:11', 'host1', '/api/v1/resource', 'ERROR', 'Database unavailable'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:11', 'host1', '/api/v1/billings', 'ERROR', 'Database unavailable'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:12', 'host1', '/api/v1/resource', 'ERROR', 'Service overload'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:12', 'host1', '/api/v1/billings', 'ERROR', 'Service overload'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:13', 'host1', '/api/v1/resource', 'ERROR', 'Connection reset'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:13', 'host1', '/api/v1/billings', 'ERROR', 'Connection reset'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:14', 'host1', '/api/v1/resource', 'ERROR', 'Timeout'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:14', 'host1', '/api/v1/billings', 'ERROR', 'Timeout'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:15', 'host1', '/api/v1/resource', 'ERROR', 'Disk full'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:15', 'host1', '/api/v1/billings', 'ERROR', 'Disk full'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:16', 'host1', '/api/v1/resource', 'ERROR', 'Network issue'),
('2024-07-11 20:00:16', 'host1', '/api/v1/billings', 'ERROR', 'Network issue');
Query data
Filter by tags and time index
You can filter data using the WHERE clause.
For example, to query the latency of host1 after 2024-07-11 20:00:15:
SELECT *
FROM grpc_latencies
WHERE host = 'host1' AND ts > '2024-07-11 20:00:15';
+---------------------+-------+-------------+---------+
| ts | host | method_name | latency |
+---------------------+-------+-------------+---------+
| 2024-07-11 20:00:16 | host1 | GetUser | 3000 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:17 | host1 | GetUser | 320 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:18 | host1 | GetUser | 3500 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:19 | host1 | GetUser | 100 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:20 | host1 | GetUser | 2500 |
+---------------------+-------+-------------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.14 sec)
You can also use functions when filtering the data.
For example, you can use approx_percentile_cont to calculate the 95th percentile of the latency grouped by the host:
SELECT
approx_percentile_cont(latency, 0.95) AS p95_latency,
host
FROM grpc_latencies
WHERE ts >= '2024-07-11 20:00:10'
GROUP BY host;
+-------------------+-------+
| p95_latency | host |
+-------------------+-------+
| 4164.999999999999 | host1 |
| 115 | host2 |
+-------------------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.11 sec)
Range query
You can use range queries to monitor latencies in real-time. For example, to calculate the p95 latency of requests using a 5-second window:
SELECT
ts,
host,
approx_percentile_cont(latency, 0.95) RANGE '5s' AS p95_latency
FROM
grpc_latencies
ALIGN '5s' FILL PREV;
+---------------------+-------+-------------+
| ts | host | p95_latency |
+---------------------+-------+-------------+
| 2024-07-11 20:00:05 | host2 | 114 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:10 | host2 | 111 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:15 | host2 | 115 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:20 | host2 | 95 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:05 | host1 | 104.5 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:10 | host1 | 4200 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:15 | host1 | 3500 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:20 | host1 | 2500 |
+---------------------+-------+-------------+
8 rows in set (0.06 sec)
Full-text search
You can use matches to search for the columns with the FULLTEXT index.
For example, to search for logs with error timeout:
SELECT
ts,
api_path,
log
FROM
app_logs
WHERE
matches(log, 'timeout');
+---------------------+------------------+--------------------+
| ts | api_path | log |
+---------------------+------------------+--------------------+
| 2024-07-11 20:00:10 | /api/v1/billings | Connection timeout |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:10 | /api/v1/resource | Connection timeout |
+---------------------+------------------+--------------------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Correlate Metrics and Logs
By combining the data from the two tables,
you can easily and quickly determine the time of failure and the corresponding logs.
The following SQL query uses the JOIN operation to correlate the metrics and logs:
WITH
metrics AS (
SELECT
ts,
host,
approx_percentile_cont(latency, 0.95) RANGE '5s' AS p95_latency
FROM
grpc_latencies
ALIGN '5s' FILL PREV
),
logs AS (
SELECT
ts,
host,
count(log) RANGE '5s' AS num_errors,
FROM
app_logs
WHERE
log_level = 'ERROR'
ALIGN '5s'
)
--- Analyze and correlate metrics and logs ---
SELECT
metrics.ts,
p95_latency,
coalesce(num_errors, 0) as num_errors,
metrics.host
FROM
metrics
LEFT JOIN logs ON metrics.host = logs.host
AND metrics.ts = logs.ts
ORDER BY
metrics.ts;
+---------------------+-------------+------------+-------+
| ts | p95_latency | num_errors | host |
+---------------------+-------------+------------+-------+
| 2024-07-11 20:00:05 | 114 | 0 | host2 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:05 | 104.5 | 0 | host1 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:10 | 4200 | 10 | host1 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:10 | 111 | 0 | host2 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:15 | 115 | 0 | host2 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:15 | 3500 | 4 | host1 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:20 | 110 | 0 | host2 |
| 2024-07-11 20:00:20 | 2500 | 0 | host1 |
+---------------------+-------------+------------+-------+
8 rows in set (0.02 sec)
GreptimeDB Dashboard
GreptimeDB offers a dashboard for data exploration and management.
Explore data
Once GreptimeDB is started as mentioned in the installation section, you can access the dashboard through the HTTP endpoint http://localhost:4000/dashboard.
To add a new query, click on the + button, write your SQL command in the command text, and then click on Run All.
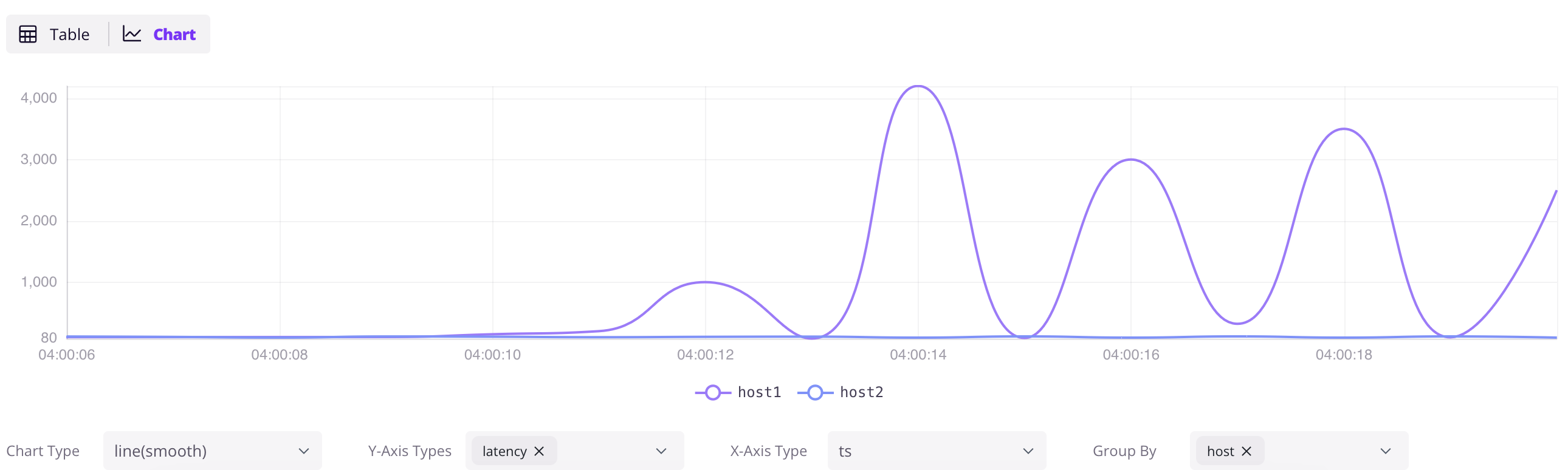
The following SQL will retrieve all the data from the grpc_latencies table.
SELECT * FROM grpc_latencies;
Then click on the Chart button in the result panel to visualize the data.
Ingest data by InfluxDB Line Protocol
Besides SQL, GreptimeDB also supports multiple protocols, one of the most popular is InfluxDB Line Protocol.
By click Ingest icon in the dashboard, you can upload data in InfluxDB Line Protocol format.
For example, paste the following data into the input box:
grpc_metrics,host=host1,method_name=GetUser latency=100,code=0 1720728021000000000
grpc_metrics,host=host2,method_name=GetUser latency=110,code=1 1720728021000000000
Then click the Write button to ingest the data to the table grpc_metrics.
The grpc_metrics table will be created automatically if it does not exist.
Next steps
You have now experienced the core features of GreptimeDB. To further explore and utilize GreptimeDB: